Related products
€36.00
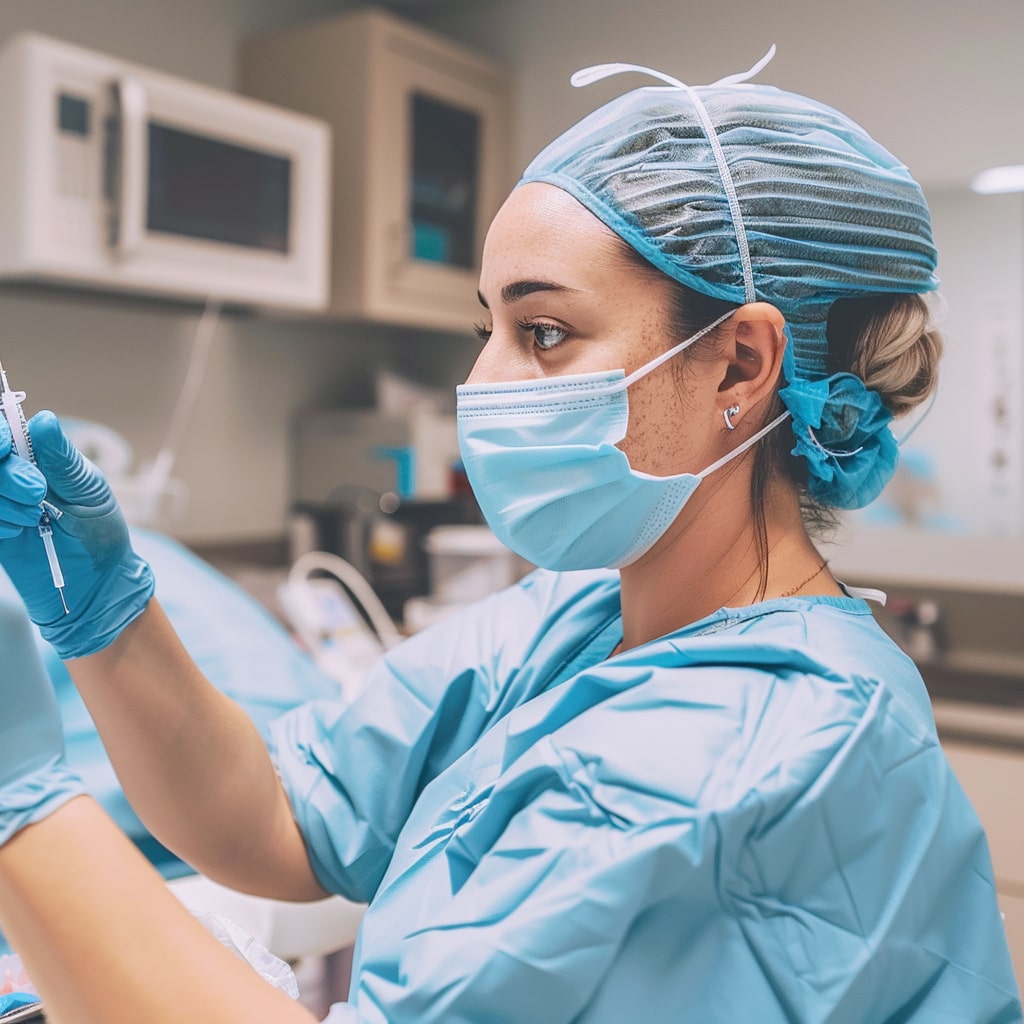
VI PRP-PRO Tubes: Revolutionary PRP Technology for Optimal Results
VI PRP-PRO:
Fast & Effective: Faster treatment process and optimal results
Safe: CE-certified, sterile, and validated for medical use
Versatile: Applicable in various medical fields
Areas of Application:
Orthopedics: Bone regeneration, sports injuries
Surgery: Wound...
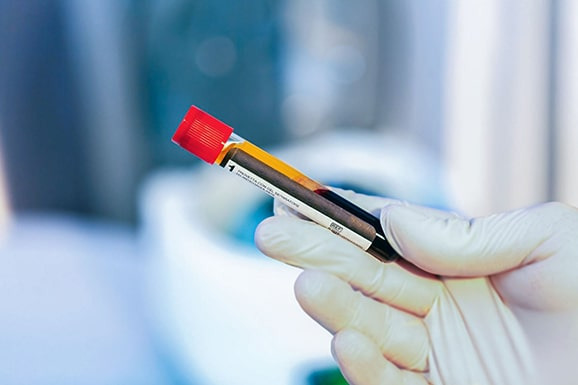
PRP
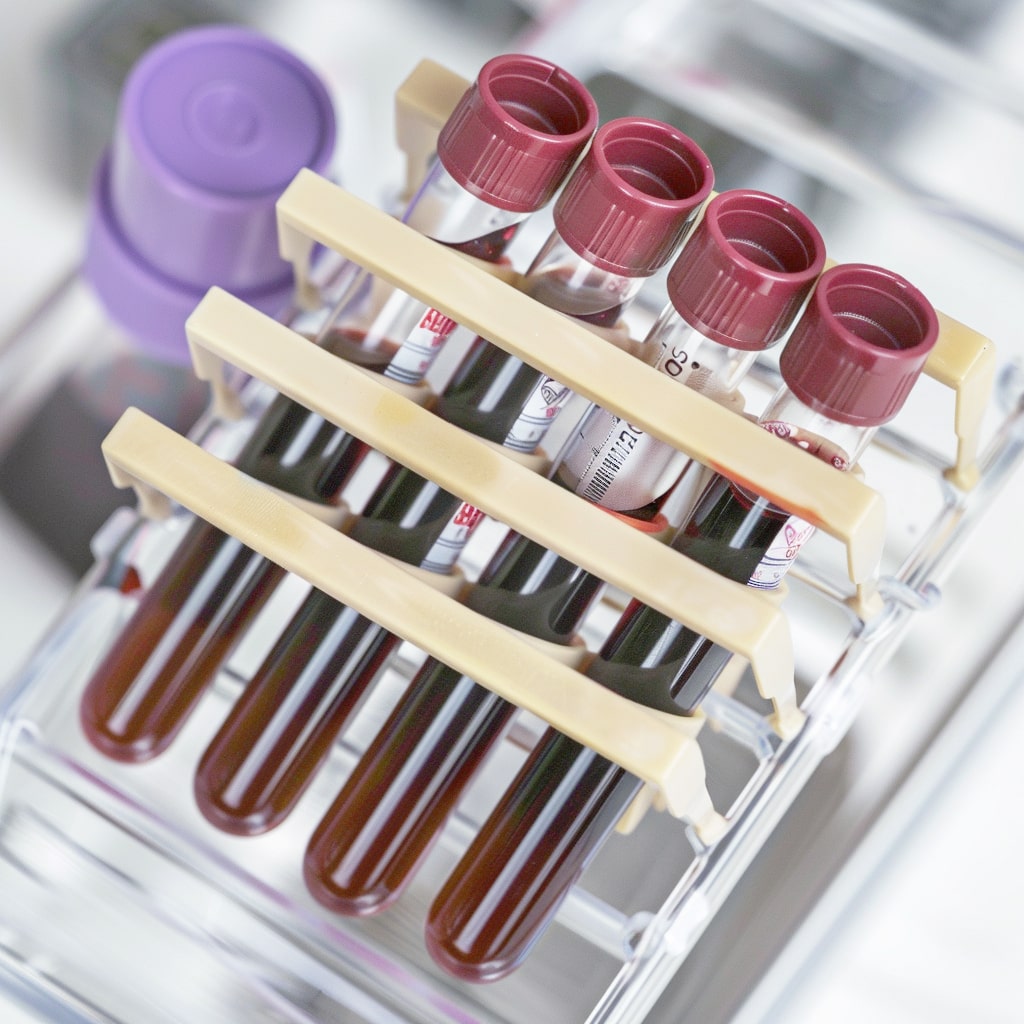
PRP tubes | Vi PRP-PRO | with Anticoagulant PU 10 pieces
PRPMED Professional Cosmetic Treatments
100101
€131.00
VI PRP-PRO | PRP Tubes – The Revolution in Plasma Treatment
The VI PRP-PRO glass tube offers a modern solution for producing platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and ensures additional stability and reliability in treatments with a wall thickness of 2.4 mm. Developed with innovative technology and EC-certified (0425-MED-004180-00), it guarantees the highest level...
Care
Vi Serum – Cosmetic care cream for demanding skin after aesthetic treatments
PRPMED Professional Cosmetic Treatments
100102
€25.95
€797.77 per Liter
Vi Serum is a high-quality, fragrance-free skincare cream for cosmetic use after intensive skin treatment, e.g. microneedling, laser or peeling. The formula has been specially developed for sensitive skin and supports the natural skin barrier with hydrating and soothing active ingredients. Made in Germany, vegan and dermatologically tested.
Contents: 25ml